9. CpG_to_gene.py¶
9.1. Description¶
This program annotates CpGs by assigning them to their putative target genes. It follows the “Basal plus extension rules” used by GREAT.
Basal regulatory domain is a user-defined genomic region around the TSS (transcription start site). By default, from TSS upstream 5 Kb to TSS downstream 1 Kb is considered as the gene’s basal regulatory domain. When defining a gene’s basal regulatory domain, the other nearby genes are ignored (which means different genes’ basal regulatory domain can be overlapped.)
Extended regulatory domain is a genomic region that is further extended from basal regulatory domain in both directions to the nearest gene’s basal regulatory domain but no more than the maximum extension (specified by ‘-e’, default - 1000 kb) in one direction. In other words, the “extension” stops when it reaches other genes’ “basal regulatory domain” or the extension limit, whichever comes first.
Basal regulatory domain and Extended regulatory domain are illustrated in below diagram.
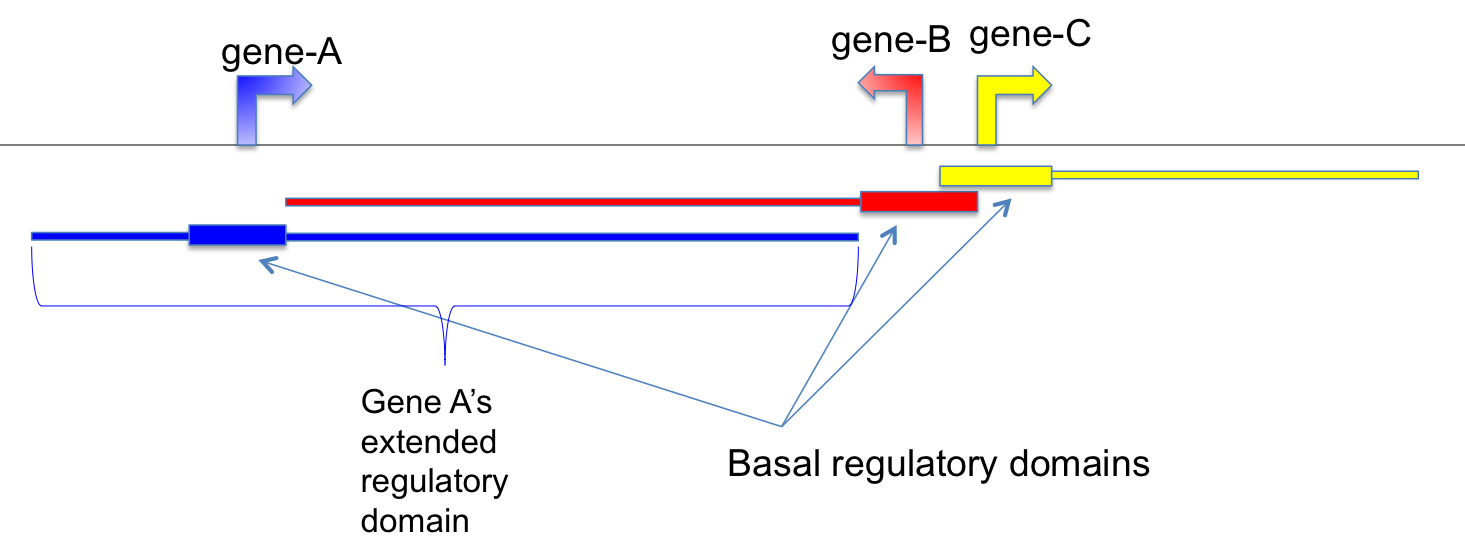
Notes
- Which genes are assigned to a particular CpG largely depends on gene annotation. A “conservative” gene model (such as Refseq curated protein-coding genes) is recommended.
- In the refgene file, multiple isoforms should be merged into a single gene.
9.2. Description¶
This program annotates CpGs by assigning them to their putative target genes. Follows the “Basel plus extension” rules used by GREAT(http://great.stanford.edu/public/html/index.php)
- Basal regulatory domain: is a user-defined genomic region around the TSS (transcription start site). By default, from TSS upstream 5kb to TSS downstream 1Kb is considered as the gene’s basal regulatory domain. When defining a gene’s “basal regulatory domain”, the other nearby genes will be ignored (which means different genes’ basal regulatory domains can be overlapped.)
- Extended regulatory domain: The gene regulatory domain is extended in both directions to the nearest gene’s “basal regulatory domain” but no more than the maximum extension (default = 1000 kb) in one direction.
9.3. Notes¶
- Which genes are assigned to a particular CpG largely depends on gene annotation. A “conservative” gene model (such as Refseq curated protein coding genes) is recommended.
- In the gene model, multiple isoforms should be merged into a single gene.
9.4. Options¶
- Options:
--version show program’s version number and exit -h, --help show this help message and exit -i INPUT_FILE, --input-file=INPUT_FILE BED3+ file specifying the C position. BED3+ file could be a regular text file or compressed file (.gz, .bz2). [required] -r GENE_FILE, --refgene=GENE_FILE Reference gene model in BED12 format (https://genome.ucsc.edu/FAQ/FAQformat.html#format1). “One gene one transcript” is recommended. Since most genes have multiple transcripts; one can collapse multiple transcripts of the same gene into a single super transcript or select the canonical transcript. -u BASAL_UP_SIZE, --basal-up=BASAL_UP_SIZE Size of extension to upstream of TSS (used to define gene’s “basal regulatory domain”). default=5000 (bp) -d BASAL_DOWN_SIZE, --basal-down=BASAL_DOWN_SIZE Size of extension to downstream of TSS (used to define gene’s basal regulatory domain). default=1000 (bp) -e EXTENSION_SIZE, --extension=EXTENSION_SIZE Size of extension to both up- and down-stream of TSS (used to define gene’s “extended regulatory domain”). default=1000000 (bp) -o OUT_FILE, --output=OUT_FILE Prefix of the output file. Two additional columns will be appended to the original BED file with the last column indicating “genes whose extended regulatory domain are overlapped with the CpG”, the 2nd last column indicating “genes whose basal regulatory domain are overlapped with the CpG”. [required]
9.5. Input files (examples)¶
9.6. Command¶
$ CpG_to_gene.py -i 850K_probe.hg19.bed3.gz -r hg19.RefSeq.union.bed.gz -o output
9.7. Output files¶
- output.associated_genes.txt
$ head output.associated_genes.txt
#The last column contains genes whose extended regulatory domain are overlapped with the CpG
#The 2nd last column contains genes whose basal regulatory domain are overlapped with the CpG
#"//" indicates no genes are found
chr1 10524 10525 DDX11L1 //
chr1 10847 10848 DDX11L1 //
chr1 10849 10850 DDX11L1 //
chr1 15864 15865 // MIR6859-1;DDX11L1
chr1 18826 18827 MIR6859-1 //
chr1 29406 29407 WASH7P;MIR1302-2 //
chr1 29424 29425 WASH7P;MIR1302-2 //
...